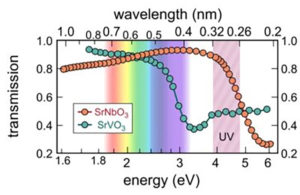
Transmission of 10-nm-thick freestanding films of SrNbO3 and SrVO3. The shaded region labeled UV indicates the spectral range the researchers used to calculate a figure of merit in transmitting UV.
UV radiation in the 200 to 300-nm range (dubbed the UV-C range) can destroy viruses, including the novel coronavirus. The problem is, doing so requires UV radiation sources putting out sufficiently high doses of UV light.
That typically means using a relatively expensive mercury gas discharge lamp. It’s possible to find sources employing LEDs that put out UV-C, but the light they put out is typically weak, too weak to do much good for disinfection purposes. One reason: Their light emission is complicated by the fact that their electrode material must also be transparent to UV-C.
Get the full story on our WTWH Media sister site Power Electronic Tips.