 According to results from the Phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study published in JAMA, the monoclonal antibody donanemab significantly slowed cognitive and functional decline in patients with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease by approximately 35% at one year compared to placebo. The trial enrolled 1736 patients across 277 research centers in 8 countries.
According to results from the Phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study published in JAMA, the monoclonal antibody donanemab significantly slowed cognitive and functional decline in patients with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease by approximately 35% at one year compared to placebo. The trial enrolled 1736 patients across 277 research centers in 8 countries.
Another monoclonal antibody, Leqembi (lecanemab) recently won FDA approval for Alzheimer’s disease treatment after showing a statistically significant 27% reduction in decline on the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale in trials.
Donanemab is an investigational plaque-clearing antibody similar to lecanemab and aducanumab, which controversially notched FDA approval in 2021 based on its plaque reduction despite inconsistent clinical efficacy data.
A look at TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2
The Phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study demonstrated that donanemab, an investigational drug, significantly slowed cognitive and functional decline in patients with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. The measured decline in iADRS and CDR-SB scores over 76 weeks was less severe in patients treated with the drug candidate compared to those given a placebo. On the iADRS scale, where lower scores indicate greater impairment, patients treated with donanemab showed a decline of 6.02 points versus a 9.27 point decline in the placebo group. These results suggest that donanemab could potentially be an effective treatment for slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms.
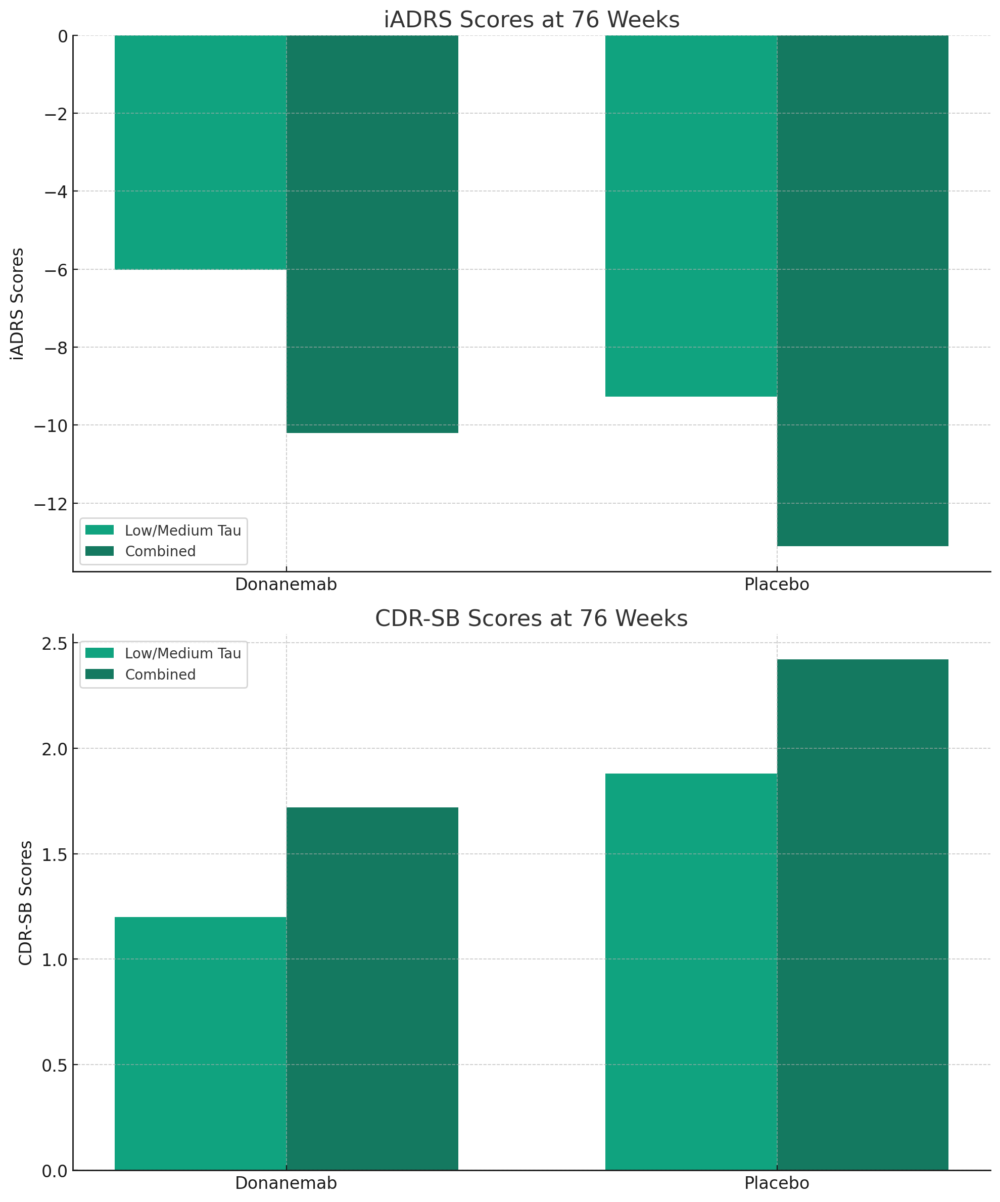
iADRS Scores at 76 Weeks: This chart shows a less severe decline in iADRS scores for patients treated with donanemab compared to those receiving placebo, indicative of slowed cognitive and functional decline. CDR-SB Scores at 76 Weeks: The graph reveals a smaller increase in CDR-SB scores in the donanemab group than the placebo group, reflecting a reduction in symptom progression in both the low/medium tau and combined population groups.
Aducanumab has failed to generate material sales. According to Evaluate, donanemab is expected to reach peak sales of around $6 billion by 2026. Donanemab reduced amyloid plaque by 84% on average and allowed discontinuation of dosing after plaque clearance for most patients by 12-18 months.
Regulatory submissions for donanemab are complete, with decisions expected by end of 2023. The monoclonal antibody provided a 39% lower Alzheimer’s progression risk over 18 months, equating to more than 7.5 additional months on average before clinical decline levels of placebo patients.