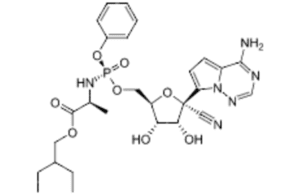
Chemical structure of the COVID-19 therapy remdesivir. Image is from Wikipedia.
Last year, FDA approved 53 drugs, leading the industry to describe 2020 as “a strong year for new drug therapy.”
There are several drugs that stand out, according to Todd Wills, the co-author of a study that analyzes how innovative drugs are based on their structure.
The drugs that follow are examples of notable innovative therapies.
[Related: Here’s what molecular shape can tell you about pharma innovation]
1. COVID-19 therapies
One of the prominent drugs that stands out as structurally novel is remdesivir from Gilead Sciences (NSDQ:GILD). The first COVID-19 treatment to win FDA approval, remdesivir (Veklury), was first developed as an Ebola treatment. But the broad-spectrum antiviral also showed promise against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Gilead recently announced that sales of remdesivir beat expectations.
While research in remdesivir began in 2009, the drug is an example of a new molecular entity — compounds the FDA hasn’t previously approved. Remdesivir “wasn’t an extension of an existing drug where they came up with COVID-19 as a new indication for it,” Wills said. “This was, at least from the lens of FDA’s terminology, a new drug.
Gilead is continuing to test the antiviral’s potential to reduce viral load in Ebola patients in a phase 2 study in West Africa.
2. Precision oncology therapies
Many of the precision oncology drugs that won FDA approval in 2020 were structurally novel.
Some of these drugs were ‘pioneers’ — that is, their molecular shape and scaffold hasn’t been used in previously approved drugs.
Notable examples of those drugs include the following:
- Orgovyx (relugolix) from Myovant Sciences (NYSE:MYOV) is the first precision oral treatment for advanced prostate cancer patients. An oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonist, Orgovyx was the subject of an international Phase 3 trial involving 934 patients with androgen-sensitive advanced prostate cancer.
- Pemazyre (pemigatinib), developed by Innovent Biologics, is the first targeted treatment for patients with cholangiocarcinoma, a bile duct cancer. The kinase inhibitor is indicated for bile duct cancer patients with a mutation in the FGFR2 gene who have had previously unsuccessful chemotherapy.
- Tabrecta (capmatinib) is the first targeted treatment for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer that have a mutation leading to mesenchymal-epithelial transition exon 14 skipping. Licensed to Novartis (NYSE: NVS) by Incyte (NSDQ:INCY), Tabrecta previously won Breakthrough Therapy Designation from FDA.
3. Gene-specific therapies
“Structurally novel drugs were also the source of multiple approved gene-specific therapies,” Wills said. Two examples include the following:
- Evrysdi (risdiplam) from Roche (SWX:RO) is the second drug and the first oral drug approved to treat spinal muscular atrophy, a rare and often fatal genetic disease affecting muscle strength and movement. The drug is indicated for adults and children two months and older.
- Retevmo (selpercatinib) from Eli Lilly (NYSE:LLY) is the first therapy for patients with lung and thyroid cancers with rearranged during transfection (RET) gene alterations. FDA approved the drug under its Accelerated Approval regulations.